Learning Objectives:
You will be able to create a valid XML document from a schema
You will be able describe how Xpath works.
Homework:
Schema Practice: Create a DTD and Schema for this XML Document
Read the XPathTutorials from W3schools
Read: Chapter 7
Answer the following Path Questions using Schedule XML:
What is one path to StartTime?
What is the path to EndTime
Answer the following Node Questions using Schedule XML:
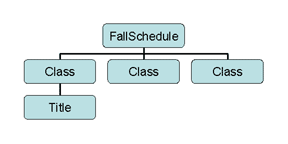
What is the Children of Fall Schedule?
Name the Ancestors of Time?
Answer the following questions using cd_catalog.xml (plus give me the path to each!)
What is the sibling of CD.
What is the Child of CD.
What is the Ancestor of CD.
/Catalog/CD/sibling::COUNTRY (give me the path directly to this element)
Topics Covered:
Xpath Notation:
Xpath gets you to a Node (a point in an XML Document). Xpath gives you ability to move from that point to another location within a document. Once at the new location, you can grab the data from that Node.
You have seven kinds of nodes that you can access:
element attribute text namespace comment processing-instruction document (root)
The more specific the path to a node the more efficient use of computer resources.
The Syntax for Xpath is similar to DOS for navigating. Xpath Axes and Operators gives you flexibility to travel the document
Using Schedule XML Document for an example of a Path inside an XML Document.
/FallSchedule/Class/Title
Document Root vs Root Element (not the same!) Document Node (Starting point for the document)
Define the path and separate it with the elements in the path with a /
// search for the node and start at that point!
@ for Attributes
AXES :: notation (example: child::class for schedule would give you Number, Title & DayOfWeek elements)
Ancestor
Parent / (Ancestor for child)
Child
Decedent / (Child of Child)
Sibling (of the Child)
Functions are built in ways to move or gather data
Position Functions: position, last, count
Node Functions: name, node (why?) , processing-instruction, comment (not well supported), text
Boolean Functions: true, false, not
Terms:
Xpath, Ancestor, AXES, Boolean, Node, Sibling, Child, Function